作者简介:
黄丹(1986-),女,四川泸县人,主治医师,医学学士,主要研究方向为老年麻醉。
目的 探讨鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定对重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者镇痛效果的影响。方法 选取2018年12月至2019年12月于重庆市云阳县人民医院确诊重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者112例,依据随机表分为吗啡组(n=56)和联合组(n=56),吗啡组给予鞘内泵注吗啡治疗,联合组在此基础上复合右美托咪定治疗,比较两组镇痛效果[视觉模拟评分法(visual analog scale,VAS)]、炎症反应[白介素6(interleukin-6,IL-6)]、肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、吗啡用量、不良反应。结果 吗啡组和联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后VAS评分、IL-6、TNF-α明显低于治疗前,联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后VAS评分、IL-6、TNF-α、吗啡日用量及不良反应率均明显低于吗啡组(全部 P<0.05)。结论 鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定可有效改善重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者镇痛效果及炎症反应,有利于减少吗啡用量及不良反应,值得临床推广。
Objective To discuss the effect of intrathecal injection of morphine combined with dexmedetomidine on the analgesic effect in patients with severe cancer pain advanced colorectal cancer.Methods 112 patients with severe cancer pain advanced colorectal cancer in Chongqing Yunyang People's Hospital were selected from December 2018 to December 2019, they were randomly divided into the morphine group (n=56) and combined group (n=56). The morphine group was treated with intrathecal injection of morphine, the combined group was treated with intrathecal injection of morphine combined with dexmedetomidine. The analgesic effect [visual analog scale (VAS)], inflammatory response [interleukin- 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)], morphine dosage and adverse reactions were compared between the two groups.Results The VAS score, IL-6 and TNF-α in the morphine group and the combined group after 1 day, 3 days and 7 days of treatment were significantly lower after treatment initiated. The VAS score, IL-6, TNF-α, the daily dosage of morphine and the incidence of adverse reactions in the combined group were all significantly lower than that in the morphine group (all P<0.05).Conclusions Intrathecal injection of morphine combined with dexmedetomidine can effectively improve the analgesic effect and inflammatory response of patients with severe cancer pain advanced colorectal cancer, and it was helpful to reduce the dosage of morphine and incidence of adverse reactions, it's worthy for further clinical promotion.
结直肠癌是临床常见的消化系统肿瘤, 早期无特异性症状, 被发现时多已处于中晚期阶段, 而癌痛是中晚期患者常见的临床症状之一, 严重影响患者生活质量, 故临床上常需进行镇痛治疗[1]。目前, 鞘内泵注吗啡是晚期结直肠癌患者常用的镇痛方法, 但仍有部分患者镇痛效果欠佳, 故如何有效改善镇痛效果是人们关注的热点[2]。而既往研究报道, 右美托咪定是一种具有镇静镇痛作用的新型麻醉药物, 近年来已被应用于围术期镇痛中, 有利于提高镇痛效果而受到关注和重视, 但关于其联合鞘内泵注吗啡在晚期结直肠癌中的应用报道较少[3]。对此, 本研究通过给予重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定治疗, 探讨其对患者镇痛效果的影响, 现报道如下。
选取2018年1月至2019年12月于重庆市云阳县人民医院确诊重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者112例, 依据随机表分为吗啡组(n=56)和联合组(n=56), 纳入标准:①经临床症状、病史、实验室、影像学、穿刺活检等检查为晚期(TNM分期为Ⅲ ~Ⅳ 期)结直肠癌[4]且伴有重度癌痛, 疼痛主要表现为持续性发作酸胀痛但偶有针刺样或电击样痛、以腰腹部、盆腔为主发部位, 视觉模拟评分法(visual analog scale, VAS)[5]> 6分; ②年龄20~80岁、意识清醒; ③无吗啡或右美托咪定过敏史、无精神病病史; ④签署知情同意书。排除标准:①有凝血功能障碍、严重出血倾向等鞘内泵注禁忌证; ②有心、肝、肾等严重病; ③孕产妇或哺乳期女性; ④有严重高血压、糖尿病或肺炎等疾病。吗啡组和联合组一般资料基本相同(P> 0.05), 见表1。本研究经重庆市云阳县人民医院伦理会批过, 伦理批号:yyky003。
| 表1 两组一般资料比较 Tab.1 Comparison of general information between the two groups |
联合组给予鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定治疗:给予禁食4 h、取侧卧位, 制定鞘内泵注方案并标记L3~L4间隙穿刺位置、右下腹部泵连接管放置位置、疼痛节段定位椎体导管到达位置(见图1A), 消毒铺巾、1%利多卡因(国药集团容生制药有限公司, 国药准字H20043676, 批号190723, 5 ml:0.1 g)局麻等准备, 采用一次性使用腰硬联合麻醉穿刺套件(河南驼人医疗器械集团有限公司, 国械注准20153080652, AS-E/Sll l型, 批号190211)以16 G穿刺针做后正中线旁1 cm穿刺, 逐层深入, 有落空感后继续穿刺见透明脑脊液流出后拔出针芯, 植入鞘内泵导管。回抽见脑脊液流出通畅后, 固定导管。用硬膜外穿刺针制作皮下隧道将导管引入标记的右下腹泵链接管穿出位置, 再次确认脑脊液流出通畅, 固定导管, 常规止血、缝合、预防感染等处理, 无菌敷贴覆盖; 连接一次性使用电子镇痛泵(江苏苏嘉医疗器械股份有限公司), 设置电子注药泵参数为自控剂量0.5 mL/次、锁定时间15 min、负荷剂量0.5 mL、背景剂量0.5 mL/h、泵注药液吗啡0.3 mg/mL(青海制药厂有限公司, 国药准字H20010315, 批号190415, 1 mL:10 mg)+右美托咪定1 μ g/mL(辰欣药业股份有限公司, 国药准字H20130027, 批号190506, 2 mL:0.2 mg)。
吗啡组仅给予鞘内泵注吗啡治疗, 即不给予复合右美托咪定治疗(电子注药泵参数中的泵注药液改为吗啡0.3 mg/mL), 其余均同联合组。
比较两组镇痛效果、炎症反应、吗啡用量、不良反应。①镇痛效果, 于治疗前及治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后采用VAS评估, Cronbach'α 信度系数为0.894, 画一分值为0~10分的直线, 评分越高则疼痛越严重; ②炎症反应, 于治疗前及治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后抽取外周静脉血3 mL并分离血清(3 000 r/min、10 min)后, 以酶联免疫吸附法检测白介素6(interleukin-6, IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子-α (tumor necrosis factor-α , TNF-α ), 试剂盒均购自上海盈公生物技术有限公司; ③吗啡用量, 记录治疗1 d、3 d、7 d时电子注药泵中的吗啡用量; ④不良反应, 记录皮肤瘙痒、便秘、尿潴留、恶心呕吐、嗜睡、呼吸抑制、血压异常、心动过缓等不良事件的发生率。
采用SPSS 22.0软件, 计数资料行χ2检验; 计量资料以($\bar{x}±s$)表示, 数据均符合正态分布, 组内治疗前后比较应该采用配对t检验, 组间比较采用独立样本t检验; P< 0.05为有统计学差异。
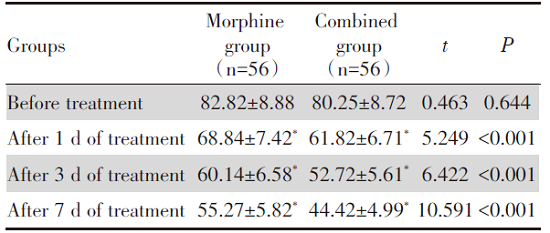
吗啡组和联合组治疗前VAS评分基本相同(P> 0.05), 吗啡组和联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后VAS评分低于治疗前, 联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后VAS评分低于吗啡组(P< 0.05), 见表2。
| 表2 两组VAS评分比较 Tab.2 Comparison of VAS scores between the two groups (points) |
吗啡组和联合组治疗前IL-6、TNF-α 基本相同(P> 0.05), 吗啡组和联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后IL-6、TNF-α 低于治疗前, 联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后IL-6、TNF-α 低于吗啡组(P< 0.05), 见表3、4。
| 表3 两组IL-6比较 Tab.3 Comparison of IL-6 between the two groups (pg/L) |
| 表4 两组TNF-α 比较 Tab.4 Comparison of TNF-α in the two groups (pg/L) |
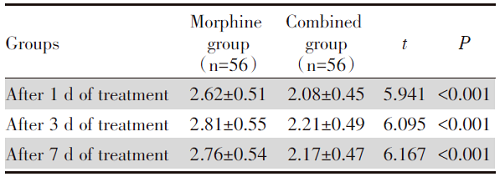
联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后吗啡日用量低于吗啡组(P< 0.05), 见表5。
| 表5 两组吗啡日用量比较 Tab.5 Comparison of daily dosage of morphine between the two groups (mg) |
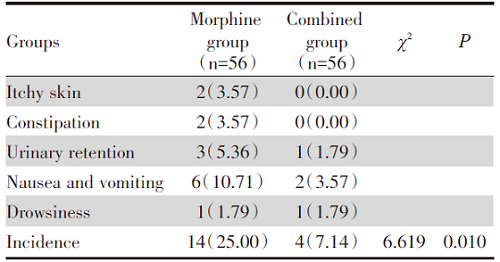
联合组不良反应率低于吗啡组(P< 0.05), 且两组均无呼吸抑制、血压异常、心动过缓等发生, 见表6。
| 表6 两组不良反应比较 Tab.6 Comparison of adverse reactions between the two groups (n/%) |
癌痛是晚期结直肠癌患者常见的临床症状, 发病率可达70%~90%, 好发于腰腹部、盆腔等部位, 其发病机制尚未明确, 主要与肿瘤异常生长压迫周围血管、神经、肌肉等组织有关, 主要表现为持续性发作酸胀痛、偶有针刺样或电击样痛, 其中约30%~50%患者存在重度疼痛, 严重危害患者生存质量[6, 7]。
目前, 药物镇痛是晚期结直肠癌重度癌痛患者常用的方法, 且世界卫生组织提出的三阶梯止痛方案已被广泛应用[8, 9]; 其中吗啡是临床常用的三阶梯止痛药物, 其为强效纯粹的阿片受体激动剂, 可激动μ 、κ 及δ 型受体而产生良好的镇痛镇静作用。而通过鞘内泵注的方式, 可直接将吗啡泵注作用于脊髓、大脑中的多种离子通道和受体, 既易通过血脑屏障, 又可避免口服所致的首过效应, 其疗效也被广泛认可[10, 11]。但在临床应用中, 随着吗啡用量增加, 药物耐受也随之增加, 且长时间大剂量用药易引起瘙痒、便秘、尿潴留、恶心呕吐、嗜睡、呼吸抑制、血压异常、心动过缓等不良反应, 从而影响患者的镇痛效果[12, 13]。
本研究对重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者实施鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定治疗, 发现吗啡组和联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后VAS评分、IL-6、TNF-α 低于治疗前, 且联合组低于吗啡组, 表明该镇痛方案能够有效改善患者镇痛效果及炎症反应。据相关研究表明, 右美托咪定是一种具有镇静镇痛、抑制交感神经兴奋、保护脑细胞和神经组织等作用的选择性α 2肾上腺素能受体激动剂, 临床上主要作为手术麻醉和术后镇痛的辅助用药, 有助于提高麻醉镇痛效果[14, 15]。此外, 既往研究报道显示, 疼痛与炎症反应网络的过度激活密切相关, 其中IL-6是可直接参与炎症反应的白介素成员, TNF-α 是具有促进炎症反应及调节IL-6生成等作用的炎症因子, IL-6、TNF-α 为临床常用的炎症反应指标, 故可反映重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者炎症状态[16, 17]。因此, 鞘内泵注吗啡镇痛, 虽能够直接作用于重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者脊髓、大脑中的离子通道和受体而产生良好的镇痛镇静作用, 有助于缓解患者疼痛症状及其所引起的炎症反应, 但可能由于重度癌痛患者的疼痛症状较为剧烈, 加之随着吗啡长时间应用, 易产生药物耐受, 部分患者易出现镇痛效果欠佳, 使患者仍存在较为严重的疼痛及其所致炎症反应。而本研究复合右美托咪定治疗, 可能由于通过鞘内泵注右美托咪定至重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者脊髓、大脑, 能够有效激动脊髓、大脑中的受体而抑制交感神经活性及疼痛信号的传导, 提高患者的镇痛效果, 并保护脑细胞和神经组织而减轻其受炎症反应的损伤, 进一步缓解患者的镇痛症状, 有利于更好、更有效地减轻疼痛所致的炎症反应, 表现为治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后VAS评分、IL-6、TNF-α 下降且炎症反应水平较低。同时, 本研究还发现联合组治疗1 d、3 d、7 d后吗啡日用量低于吗啡组, 表明鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定能够有效减少重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者的吗啡用量。这可能由于在鞘内泵注吗啡治疗中, 复合右美托咪定能够提高对重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者的镇静镇痛效果, 并抑制炎症反应, 有利于更好、更有效地缓解患者癌痛症状而减轻了其对鞘内泵注药物镇痛的需求, 从而减少了吗啡用量。
此外, 本研究还发现联合组不良反应率低于吗啡组, 表明鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定能够有效减少重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者的不良反应。这可能由于鞘内联合泵注减少了吗啡的用量, 从而减少皮肤瘙痒、便秘、尿潴留、恶心呕吐、嗜睡等不良反应的发生, 提高了镇痛治疗的安全性。而本研究发现吗啡组和联合组均无呼吸抑制、血压异常、心动过缓等严重不良反应, 这可能与本研究对晚期结直肠癌患者均采用了鞘内泵注的方式, 避免口服吗啡所致的首过效应, 且用量较全身性用药少[18]。
综上所述, 鞘内泵注吗啡复合右美托咪定可有效改善重度癌痛晚期结直肠癌患者镇痛效果及炎症反应, 有利于减少吗啡用量及不良反应, 值得临床推广。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|