谢旭东(1987-),男,陕西铜川人,医学学士,主治医师,主要研究方向为消化道早期癌症内镜诊治。
目的 研究血清长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,LncRNA)-HOTAIR在急性胰腺炎患者中的表达情况及其潜在的临床意义。方法 选取2018年1月至2019年12月在铜川市人民医院因“急性胰腺炎”住院的患者共80例纳入本次研究,根据患者是否达到“重症急性胰腺炎”的诊断标准,将患者分为轻症急性胰腺炎组(mild acute pancreatitis,MAP)、中重症急性胰腺炎组(moderate severe acute pancreatitis,MSAP)和重症急性胰腺炎组(severe acute pancreatitis,SAP),其中MAP组20例,MSAP组20例,SAP组40例。另选取同时期在铜川市人民医院进行体检的健康志愿者40例纳入对照组。比较四组受试者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平及其他炎症相关指标,如C反应蛋白(C-reaction protein,CRP)、降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)、淀粉酶、脂肪酶等;分析血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平与上述炎症相关指标的关系。评估血清LncRNA-HOTAIR对诊断急性胰腺炎的效能。结果 四组患者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量存在显著差异( P<0.05),SAP组最高,对照组最低。SAP组的CRP、PCT、血清淀粉酶、血清脂肪酶水平均显著高于其他三组( P<0.05)。将MAP组、MSAP组和SAP组患者的数据合并进入Pearson相关性分析,发现急性胰腺炎患者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平与CRP( r=0.231, P=0.001)、PCT(r=0.192, P=0.003)成正相关,但与血清淀粉酶、脂肪酶无显著相关性。运用受试者工作特征曲线 (receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线分析,发现当血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量>1.292时,诊断急性胰腺炎的灵敏度为0.750,特异度为0.725,曲线下面积(Area under curve,AUC)为0.783。运用ROC曲线分析血清LncRNA-HOTAIR对重症急性胰腺炎的诊断效能发现当LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量>1.590时,其灵敏度为0.606,特异度为0.936,AUC为0.837。结论 急性胰腺炎患者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平显著升高,与感染的严重程度成正相关。此外,血清LncRNA-HOTAIR对诊断急性胰腺炎特别是重症急性胰腺炎有一定价值,同时可进一步区分急性胰腺炎的严重程度。
Objective To study the expression of serum long non-coding RNA (LncRNA)-HOTAIR in patients with acute pancreatitis and to explore its clinical significance.Methods A total of 80 patients with “acute pancreatitis” admitted to Tongchuan People's hospital from January 2018 to December 2019 were selected and divided into mild acute pancreatitis (MAP), moderate severe acute pancreatitis (MSAP) and severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) according to whether the patients met the diagnostic criteria of “severe acute pancreatitis”, including 20 cases in MAP group, 20 cases in MSAP group and 40 cases in SAP group. Another 40 healthy volunteers who had physical examination in Tongchuan People's hospital during the same period were selected as the control group. The levels of serum LncRNA-HOTAIR and other inflammation related indexes, such as C-reaction protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), amylase and lipase, were compared among the four groups, and the relationship between the serum LncRNA-HOTAIR level and the above inflammation related indexes was analyzed. Intend to evaluate the efficacy of serum LncRNA-HOTAIR in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.Results The relative expression of serum LncRNA-HOTAIR was significantly different in the four groups ( P<0.05), with the highest in the SAP group and the lowest in the control group. The levels of CRP, PCT, serum amylase and serum lipase in the SAP group were significantly higher than those in the other two groups ( P<0.05). After merging the data of patients in the MAP and SAP groups, it was found that the serum LncRNA-HOTAIR level of patients with acute pancreatitis was positively correlated with CRP ( r=0.231, P=0.001) and PCT ( r=0.192, P=0.003), but was not significantly correlated with serum amylase and lipase. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that when the relative expression of serum LncRNA-HOTAIR was >1.292, the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis were 0.750 and 0.725, and the area under curve (AUC) was 0.783. ROC curve was used to analyze the diagnostic efficacy of serum LncRNA-HOTAIR in severe acute pancreatitis. It was found that when the relative expression of LncRNA-HOTAIR was >1.590, its sensitivity was 0.606, specificity was 0.936, and AUC was 0.837.Conclusions Serum LncRNA-HOTAIR levels were significantly elevated in patients with acute pancreatitis, and were positively correlated with the severity of the infection. In addition, serum LncRNA-HOTAIR has certain value in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis, especially severe acute pancreatitis, and can further distinguish the severity of acute pancreatitis.
急性胰腺炎是常见的急腹症之一, 若发展为重症急性胰腺炎, 则死亡率极高, 因此早期诊断、早期治疗是急性胰腺炎治疗的关键[1]。长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA, LncRNA)是一类长度大于200 nt但无法编码翻译成蛋白质的RNA分子, LncRNA-HOTAIR是第一个被发现具有反义调控作用的LncRNA[2]。研究发现, LncRNA-HOTAIR在恶性肿瘤中高表达, 能够调控肿瘤细胞的各项生物学功能; 此外, LncRNA-HOTAIR被发现在类风湿性关节炎、急性肺损伤等均显著升高[3, 4, 5]。但其在急性胰腺炎中的作用目前少有报道, 因此, 本研究拟探讨血清LncRNA-HOTAIR在急性胰腺炎患者中的表达情况及其潜在的临床意义。
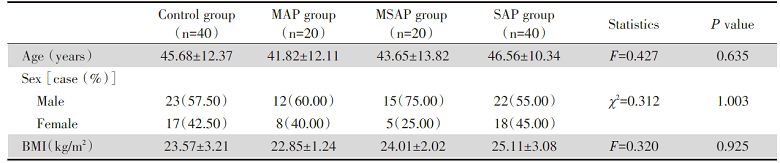
选取2018年1月至2019年12月在铜川市人民医院因“ 急性胰腺炎” 住院的患者共80例纳入本次研究, 根据患者是否达到“ 重症急性胰腺炎” 的诊断标准, 将患者分为轻症急性胰腺炎组(mild acute pancreatitis, MAP)、中重症急性胰腺炎组(moderate severe acute pancreatitis, MSAP)和重症急性胰腺炎组(severe acute pancreatitis, SAP), 其中MAP组20例, MSAP组20例, SAP组40例。“ 重症急性胰腺炎” 的诊断符合《2019年世界急诊外科学会重症急性胰腺炎诊治共识》中的诊断标准[6]。排除标准:(1)合并有糖尿病、胰腺占位等胰腺疾病; (2)非铜川市人民医院首诊患者, 入院前已接受过相应治疗; (3)合并有其他器官或组织感染, 感染与本次胰腺炎无关; (4)既往有多次胰腺炎发作病史; (5)患者或其家属不愿意参与本次研究。另选取同时期在铜川市人民医院进行体检的健康志愿者40例纳入对照组。所有受试者均在铜川市人民医院于临床干预前抽取2 mL静脉血, 送检验科检测。所有受试者纳入研究前均已知情, 并签署知情同意书, 本研究得到铜川市人民医院医学伦理委员会批准。四组受试者的一般资料比较, 差异无统计学意义(P> 0.05), 具有可比性, 见表1。
| 表1 四组受试者一般资料比较 Tab.1 Comparison of general information of the four groups of subjects |
采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase-chain-reaction, RT-qPCR)检测血清中LncRNA-HOTAIR的含量。运用Thermo 2x SYBR Green qPCR Mix, 根据试剂盒说明配置检测所需的RT-PCR体系, 在ABI 7500 Real-Time PCR System上进行RT-PCR, 反应程序为:95 ℃ 20 s; 95 ℃ 10 s, 60 ℃ 30 s, 40个循环; 以β -actin作为内参, 采用2-∆ ∆ Ct法计算LncRNA-HOTAIR的表达量。所测基因的引物序列见表2。
| 表2 β -actin和LncRNA-HOTAIR引物序列 Tab.2 Primer sequence of β -actin and LncRNA-HOTAIR |
比较四组受试者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平及其他炎症相关指标, 如C反应蛋白(C-reaction protein, CRP)、降钙素原(procalcitonin)、淀粉酶、脂肪酶等; 分析血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平与上述炎症相关指标的关系。评估血清LncRNA-HOTAIR对诊断急性胰腺炎的效能。
采用SPSS 22.0软件进行数据统计和分析; 计量资料采用均数± 标准差的形式表示, 多组间采用One way ANOVA进行检验, 组组间采用LSD法比较; 计数资料采用频数(率)的形式表示, 组间采用卡方检验进行比较。采用Pearson检验检测两项指标间的相关性。运用受试者工作特征(receiver operation characteristic, ROC)曲线评估指标的效能。定义P< 0.05为差异存在统计学意义。
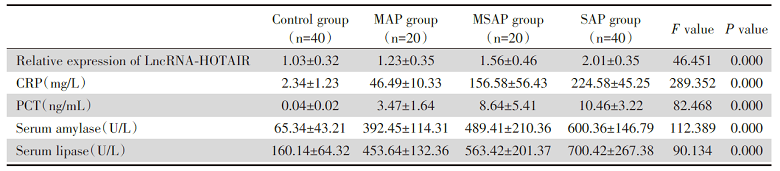
SAP患者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量最高, 对照组最低(P< 0.05)。SAP组的其他感染指标水平均显著高于其他三组(P< 0.05), 详见表3。
| 表3 急性胰腺炎患者与血清LncRNA-HOTAIR表达及其他炎症相关指标比较 Tab.3 Comparison of LncRNA-HOTAIR expression and other inflammation related indexes in patients with acute pancreatitis |
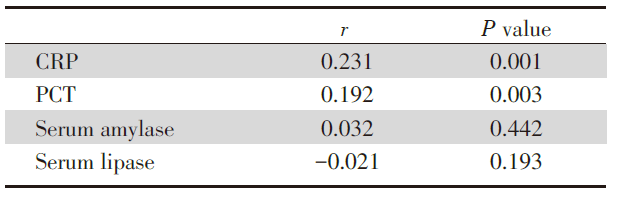
急性胰腺炎患者中血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平与CRP(r=0.231, P=0.001)、PCT(r=0.192, P=0.003)成正相关, 但与血清淀粉酶、脂肪酶无显著相关性, 详见表4。
| 表4 急性胰腺炎患者中血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平与炎症指标的关系 Tab.4 The relationship between serum LncRNA-HOTAIR levels and inflammation indexes in patients with acute pancreatitis |
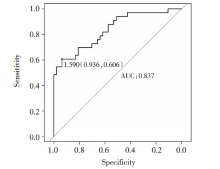
运用ROC曲线分析, 当血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量> 1.292时, 曲线下面积(area under curve, AUC)为0.783, 见图1, 即当血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量> 1.292时, 对急性胰腺炎有一定的诊断价值。而当LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量> 1.590时, 对重症急性胰腺炎诊断的AUC为0.837, 见图2。因此, 当血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量> 1.590时, 对重症急性胰腺炎有较高的诊断价值, 可进一步区分急性胰腺炎的严重程度。
 | 图1 血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平诊断急性胰腺炎的ROC分析Fig.1 ROC analysis of serum LncRNA-HOTAIR level in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis |
LncRNA是一类长度大于200nt, 无法翻译成蛋白质的RNA。既往认为LncRNA是生物进化中的遗传垃圾, 但近年来越来越多的研究发现, LncRNA虽然不具备编码功能, 但其能够在表观遗传调控、转录调控以及转录后调控方面调控目的基因的表达, 还能够通过与组蛋白结合调控下游基因的转录活性, 以及改变蛋白质在细胞中的定位从而影响蛋白质的功能[7, 8]。LncRNA-HOTAIR是基因HOX的反义转录RNA, 具有反式调控作用。研究发现其可以调控H3K27me3等组蛋白从而影响下游基因及信号通路, 影响细胞的多种生物学功能, 在肿瘤中起到重要的作用[9, 10, 11, 12]。一方面, 有研究证实, 胰腺导管腺癌中LncRNA-HOTAIR的水平明显升高[13]。另一方面, HOTAIR的功能多态性会影响人群胰腺癌的易感性[14]。但是LncRNA-HOTAIR在胰腺炎中的研究目前较少, 由此, 我们通过探索LncRNA-HOTAIR在胰腺炎中的功能, 可能为临床上对胰腺炎的治疗奠定一定基础。
本次研究探讨了LncRNA-HOTAIR在急性胰腺炎患者中的表达, 发现急性胰腺炎患者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平显著高于正常人群, 提示LncRNA-HOTAIR可能与急性胰腺炎相关。刘芹等在大鼠中的研究发现, LncRNA-HOTAIR在脂多糖诱导的脓毒血症大鼠中明显升高, 且这一现象与TLR4依赖性信号通路所致的氧化应激有关[15]。此外, Obaid等研究指出, LncRNA-HOTAIR是巨噬细胞中活化NF-kB通路的重要分子, 与炎症、免疫应答等有密切关系[16]。结合本次研究结果, 提示LncRNA-HOTAIR可能与急性胰腺炎的免疫应答、氧化应激等过程有关。
通过与常用炎症指标的相关性分析, 本研究发现, 血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平与CRP、PCT水平正相关, 这也进一步说明, LncRNA-HOTAIR可能参与了感染炎症反应, 其水平可能一定程度上反映患者感染的严重程度。但本次研究发现血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平与血清淀粉酶和脂肪酶的水平无明显相关性。淀粉酶和脂肪酶与胰腺功能相关, 重症急性胰腺炎患者由于剩余胰腺细胞总量少, 其血清淀粉酶、脂肪酶并不一定较高, 严重者可能进一步降低[17]。因此, 血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平比血清淀粉酶、脂肪酶等指标对于反映急性胰腺炎的严重程度更敏感。
为了进一步探讨血清LncRNA-HOTAIR在急性胰腺炎中的诊断价值, 本次研究运用ROC曲线分析发现当血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量> 1.292时, 灵敏度为0.750, 特异度为0.725, AUC为0.783; 而若患者已诊断为急性胰腺炎时, 当血清LncRNA-HOTAIR相对表达量> 1.590时, 其灵敏度为0.606, 特异度为0.936, AUC为0.837。说明, 血清LncRNA-HOTAIR能够协助诊断急性胰腺炎特别是重症急性胰腺炎, 可进一步区分急性胰腺炎的严重程度。
急性胰腺炎患者血清LncRNA-HOTAIR水平显著升高, 与感染的严重程度成正相关。此外, 血清LncRNA-HOTAIR对诊断急性胰腺炎特别是重症急性胰腺炎有一定价值, 同时可进一步区分急性胰腺炎的严重程度。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|